Logs Collected in Sidecar Method¶
Although it is not recommended to use the sidecar method to collect container logs by default, in some limited scenarios, only the sidecar method can be used to collect container logs. Here we give an example for reference.
General Idea¶
As shown below:
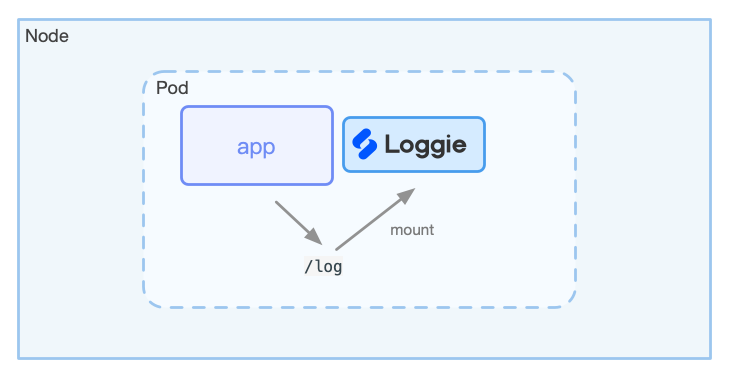
Loggie and the business container are deployed in the same Pod, and the same log file volume needs to be mounted. In addition, the configuration of Loggie can be mounted to the container through configMap. Loggie collects the logs of the container according to the provided configuration file in configMap, and send them to the backend.
Injecte Loggie Sidecar¶
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: tomcat
name: tomcat
namespace: default
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: tomcat
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: tomcat
spec:
containers:
- name: tomcat
image: tomcat
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /usr/local/tomcat/logs
name: log
- name: loggie
args:
- -config.system=/opt/loggie/loggie.yml
- -config.pipeline=/opt/loggie/pipeline.yml
image: loggieio/loggie:main
volumeMounts:
# same log volume
- mountPath: /usr/local/tomcat/logs
name: log
# loggie configuration configMap
- mountPath: /opt/loggie
name: loggie-config
# loggie data
- mountPath: /data
name: registry
volumes:
- emptyDir: {}
name: log
- emptyDir: {}
name: registry
- name: loggie-config
configMap:
name: tomcat-loggie-config
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: tomcat-loggie-config
namespace: default
data:
loggie.yml: |
loggie:
reload:
enabled: true
period: 10s
monitor:
logger:
period: 30s
enabled: true
listeners:
filesource: ~
filewatcher: ~
reload: ~
sink: ~
http:
enabled: true
port: 9196
pipeline.yml: |
pipelines:
- name: "tomcat"
sources:
- type: "file"
name: "tomcatlog"
paths:
- "/usr/local/tomcat/logs/*.log"
fields:
namespace: default
deployment: tomcat
fieldsFromEnv:
podname: HOSTNAME
sink:
type: "dev"
printEvents: true
codec:
pretty: true
You can use the loggie sidecar to collect container logs by referring to the above exapmle. Node:
- At present, it is not recommended to enable kubernetes discovery in the configuration file. Since Kubernetes will be requested after opening, when there are many Pods, it will cause certain pressure on Kubernetes. Therefore, LogConfig CRD cannot be used, and configMap needs to be used to mount the configuration file.
- Since Kubernetes discovery is not used, the fields here will not be automatically added with the Pod's meta information, and need to be obtained from the Pod's environment variables using the fieldsFromEnv.
Tips
- Fixed information such as namespace can be configured in fields, or referenced to env by using the downward API.
- The Env environment variable obtained by fieldsFromEnv is not limited to the env field configured in the Pod yaml, but any environment variable in the Loggie container. We can execute the
envcommand in the container to view it.
- Modifying the parameters in the configMap will take a period of time to be refreshed to the Pod. If you want it to take effect immediately, you need to rebuild the Pod. Please pay attention to whether it will affect the business.
Info
In the future, Loggie will support automatic Sidecar injection and automatic generation of ConfigMap mounts through LogConfig, so as to achieve the same experience as using DaemonSet.